W3schools Primary Key Er Diagrams Examples
Working with ER Diagrams
ER Diagram is a visual representation of data that describes how data is related to each other. In ER Model, we disintegrate data into entities, attributes and setup relationships between entities, all this can be represented visually using the ER diagram.
For example, in the below diagram, anyone can see and understand what the diagram wants to convey: Developer develops a website, whereas a Visitor visits a website.

Components of ER Diagram
Entitiy, Attributes, Relationships etc form the components of ER Diagram and there are defined symbols and shapes to represent each one of them.
Let's see how we can represent these in our ER Diagram.
Entity
Simple rectangular box represents an Entity.

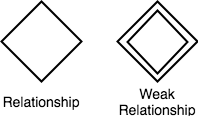
Relationships between Entities - Weak and Strong
Rhombus is used to setup relationships between two or more entities.
Attributes for any Entity
Ellipse is used to represent attributes of any entity. It is connected to the entity.

Weak Entity
A weak Entity is represented using double rectangular boxes. It is generally connected to another entity.

Key Attribute for any Entity
To represent a Key attribute, the attribute name inside the Ellipse is underlined.

Derived Attribute for any Entity
Derived attributes are those which are derived based on other attributes, for example, age can be derived from date of birth.
To represent a derived attribute, another dotted ellipse is created inside the main ellipse.

Multivalued Attribute for any Entity
Double Ellipse, one inside another, represents the attribute which can have multiple values.

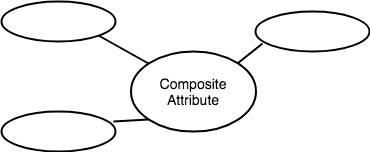
Composite Attribute for any Entity
A composite attribute is the attribute, which also has attributes.
ER Diagram: Entity
An Entity can be any object, place, person or class. In ER Diagram, an entity is represented using rectangles. Consider an example of an Organisation- Employee, Manager, Department, Product and many more can be taken as entities in an Organisation.

The yellow rhombus in between represents a relationship.
ER Diagram: Weak Entity
Weak entity is an entity that depends on another entity. Weak entity doesn't have anay key attribute of its own. Double rectangle is used to represent a weak entity.

ER Diagram: Attribute
An Attribute describes a property or characterstic of an entity. For example, Name, Age, Address etc can be attributes of a Student. An attribute is represented using eclipse.

ER Diagram: Key Attribute
Key attribute represents the main characterstic of an Entity. It is used to represent a Primary key. Ellipse with the text underlined, represents Key Attribute.

ER Diagram: Composite Attribute
An attribute can also have their own attributes. These attributes are known as Composite attributes.

ER Diagram: Relationship
A Relationship describes relation between entities. Relationship is represented using diamonds or rhombus.

There are three types of relationship that exist between Entities.
- Binary Relationship
- Recursive Relationship
- Ternary Relationship
ER Diagram: Binary Relationship
Binary Relationship means relation between two Entities. This is further divided into three types.
One to One Relationship
This type of relationship is rarely seen in real world.

The above example describes that one student can enroll only for one course and a course will also have only one Student. This is not what you will usually see in real-world relationships.
One to Many Relationship
The below example showcases this relationship, which means that 1 student can opt for many courses, but a course can only have 1 student. Sounds weird! This is how it is.

Many to One Relationship
It reflects business rule that many entities can be associated with just one entity. For example, Student enrolls for only one Course but a Course can have many Students.

Many to Many Relationship

The above diagram represents that one student can enroll for more than one courses. And a course can have more than 1 student enrolled in it.
ER Diagram: Recursive Relationship
When an Entity is related with itself it is known as Recursive Relationship.

ER Diagram: Ternary Relationship
Relationship of degree three is called Ternary relationship.
A Ternary relationship involves three entities. In such relationships we always consider two entites together and then look upon the third.

For example, in the diagram above, we have three related entities, Company, Product and Sector. To understand the relationship better or to define rules around the model, we should relate two entities and then derive the third one.
A Company produces many Products/ each product is produced by exactly one company.
A Company operates in only one Sector / each sector has many companies operating in it.
Considering the above two rules or relationships, we see that although the complete relationship involves three entities, but we are looking at two entities at a time.
Source: https://www.studytonight.com/dbms/er-diagram.php
Posted by: meredithburgenere0194515.blogspot.com
Post a Comment for "W3schools Primary Key Er Diagrams Examples"